Welcome to the comprehensive guide on Canada’s time zones, a crucial aspect for anyone planning trips, making international calls, or scheduling virtual meetings across this vast country. With its extensive geographical spread, Canada encompasses multiple time zones, each holding unique characteristics and playing a significant role in the nation’s daily life. This guide delves into the intricacies of Canada’s time zones, exploring the Canadian Time Zones Map and discussing the significance of these time divisions. Understanding these time zones is essential for coordinating activities across Canada’s vast distances, minimizing confusion, and ensuring accurate scheduling.
What are Time Zones, and why are they important?
Time zones are geographical regions with the same standard time. They are essential for coordinating activities across vast distances, minimizing confusion, and ensuring accurate scheduling. Time zones are based on the rotation of the Earth and are divided into 24 sections, each approximately 15 degrees of longitude apart.
Canada’s Time Zones Overview
Canada extends across six primary time zones: Pacific Time Zone (PT), Mountain Time Zone (MT), Central Time Zone (CT), Eastern Time Zone (ET), Atlantic Time Zone (AT), and Newfoundland Time Zone (NT). Let’s explore each time zone and its notable features:
Pacific Time Zone (PT)
The Pacific Time Zone, or PT, covers British Columbia and the Yukon Territory. Major cities in this time zone include Vancouver, Victoria, and Whitehorse. PT is eight hours behind Coordinated Universal Time (UTC-8) during standard time and seven hours behind (UTC-7) during daylight saving time. For more information and a time zone map, follow the related links.
Mountain Time Zone (MT)
The Mountain Time Zone, or MT, encompasses Alberta, some regions of British Columbia, and parts of the Northwest Territories. Cities like Calgary and Edmonton follow this time zone. MT is seven hours behind (UTC-7) during standard time and six hours behind (UTC-6) during daylight saving time. For more information and a time zone map, follow the related links.
Central Time Zone (CT)
The Central Time Zone, commonly called CT, covers Saskatchewan, Manitoba, and parts of Ontario and Nunavut. Notable cities in this time zone include Regina, Winnipeg, and Thunder Bay. CT is six hours behind (UTC-6) during standard time and five hours behind (UTC-5) during daylight saving time. For more information and a time zone map, follow the related links.
Eastern Time Zone (ET)
The Eastern Time Zone, denoted as ET, spans Ontario, Quebec, and parts of Nunavut. Major cities like Toronto, Ottawa, and Montreal adhere to this time zone. ET is five hours behind (UTC-5) during standard time and four hours behind (UTC-4) during daylight saving time. For more information and a time zone map, follow the related links.
Atlantic Time Zone (AT)
The Atlantic Time Zone, also known as AT, covers the Atlantic provinces of Canada, including New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, Newfoundland, and Labrador. Cities such as Halifax and St. John’s are in this time zone. AT is four hours behind (UTC-4) during standard time and three hours behind (UTC-3) during daylight saving time. For more information and a time zone map, follow the related links.
Newfoundland Time Zone (NT)
The Newfoundland Time Zone, denoted as NT is unique to the province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It is half an hour ahead of the Atlantic Time Zone. NT is 3.5 hours behind (UTC-3:30) during standard time and 2.5 hours behind (UTC-2:30) during daylight saving time. For more information and a time zone map, follow the related links.
Canadian Time Zones Map
Canada is a vast country that spans multiple time zones, each with distinct characteristics. Exploring the divisions of Canada’s time zones is essential for understanding the country’s temporal landscape and effectively planning activities across its vast expanse.
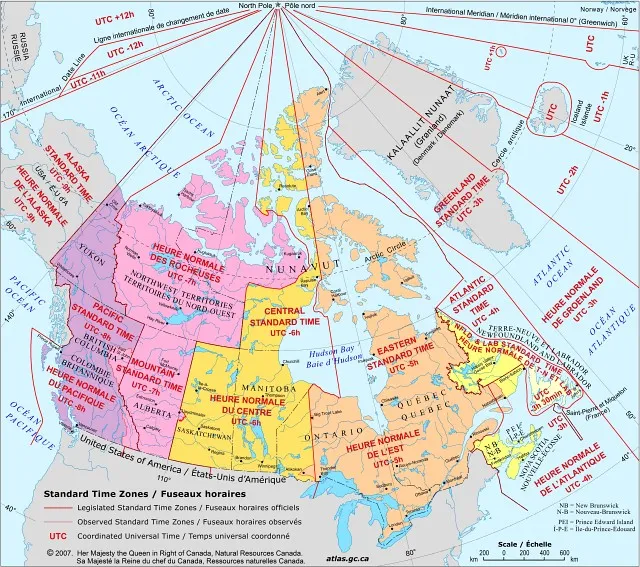
Let’s delve into the different time zones in Canada and their significance:
- Pacific Time Zone (PT): The Pacific Time Zone, abbreviated as PT, is the westernmost time zone in Canada. It covers regions such as British Columbia and the Yukon Territory. Major cities within this time zone include Vancouver, Victoria, and Whitehorse. Pacific Standard Time (PST) is observed during the non-daylight saving period, where PT is eight hours behind Coordinated Universal Time (UTC-8). During daylight saving time, it shifts to Pacific Daylight Time (PDT), seven hours behind (UTC-7).
- Mountain Time Zone (MT): Moving eastward, we enter the Mountain Time Zone (MT), which encompasses regions like Alberta, certain areas of British Columbia, and parts of the Northwest Territories. Cities such as Calgary and Edmonton observe this time zone. Mountain Standard Time (MST) is observed during standard time, with MT being seven hours behind (UTC-7). It shifts to Mountain Daylight Time (MDT) during daylight saving time, six hours behind (UTC-6).
- Central Time Zone (CT): Continuing eastward, we arrive at the Central Time Zone (CT), which covers Saskatchewan, Manitoba, and parts of Ontario and Nunavut. Notable cities within this time zone include Regina, Winnipeg, and Thunder Bay. Central Standard Time (CST) is observed during standard time, with CT being six hours behind (UTC-6). It shifts to Central Daylight Time (CDT) during daylight saving time, five hours behind (UTC-5).
- Eastern Time Zone (ET): Moving east, we encounter the Eastern Time Zone (ET), encompassing Ontario, Quebec, and parts of Nunavut. Major cities such as Toronto, Ottawa, and Montreal adhere to this time zone. Eastern Standard Time (EST) is observed during standard time, with ET being five hours behind (UTC-5). During daylight saving time, it shifts to Eastern Daylight Time (EDT), which is four hours behind (UTC-4).
- Atlantic Time Zone (AT): Continuing eastward, we reach the Atlantic Time Zone (AT), which includes the Atlantic provinces of Canada, namely New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, and Newfoundland and Labrador. Cities such as Halifax and St. John’s fall within this time zone. Atlantic Standard Time (AST) is observed during standard time, with AT being four hours behind (UTC-4). During daylight saving time, it shifts to Atlantic Daylight Time (ADT), which is three hours behind (UTC-3).
- Newfoundland Time Zone (NT): Lastly, we encounter the Newfoundland Time Zone (NT), which is unique to the province of Newfoundland and Labrador. Newfoundland Standard Time (NST) is observed during standard time. NT is 3 hours and 30 minutes behind Greenwich Mean Time (GMT-3:30). During daylight saving time, it shifts to Newfoundland Daylight Time (NDT), which is 2 hours and 30 minutes behind (GMT-2:30). The island of Newfoundland decided to set its clock at the halfway point of its time zone to accommodate its unique geographic location.
It’s worth noting that many parts of Canada do not strictly adhere to the official time zone boundaries. Some regions choose to adopt the time of a neighboring zone to facilitate trade and coordination between adjacent areas. This is particularly common in eastern British Columbia, where Mountain time is often used instead of Pacific time, aligning with the rest of the province.
To visualize the divisions and boundaries of Canada’s time zones, refer to the Canadian Time Zones Map. This map clearly represents the time zones, allowing you to effectively plan activities, schedule meetings, and navigate time differences across the country.
Understanding Canada’s time zones is crucial for anyone living in or traveling to the country. It ensures accurate scheduling, prevents confusion, and facilitates efficient coordination of activities. Whether you’re exploring the stunning landscapes of British Columbia or immersing yourself in the vibrant culture of Quebec, being aware of the time zones will enhance your experience in the Great White North.
By familiarizing yourself with the Canadian Time Zones Map and the distinctive features of each time zone, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the temporal landscape of Canada and make the most of your time in this diverse and beautiful country.
Importance of Time Zones in Canada
Time zones are crucial in various aspects of daily life and travel in Canada. They affect transportation schedules, international communications, and the coordination of business operations across the country. Being aware of the time differences enables efficient planning and prevents misunderstandings caused by scheduling conflicts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, grasping the concept of Canada’s time zones is vital for anyone living in or traveling across this diverse country. The Canadian Time Zones Map is an invaluable tool, visually representing the time divisions and aiding in planning and coordinating activities. Whether it’s for scheduling meetings, catching flights, or connecting with friends and family across different regions, being mindful of these time zones is key. Remember to consider these time differences in your plans to ensure smooth and efficient experiences in the Great White North.